好多人做了这个小游戏的一键通关功能,正好最近在玩C#,就用wpf做了个
在爬取qq空间相册过程中尝试去理解各个参数的意义,最后发现g_tk参数的来源不明,而且此参数不能去掉,必须携带,后面在腾讯的js中得到g_tk的加密算法:
def get_g_tk(skey: str):
h = 5381
for i in range(len(skey)):
h += (h << 5) + ord(skey[i])
return h & 0x7fffffff在这里我直接写成了python版本,计算gtk需要skey参数,skey是在登录时保存到本地的cookies中的,用于用户身份权限的认证。

在做情侣空间这个项目的相册功能时,想直接用qq相册的接口去获得之前上传的照片,在开发者工具下可以很容易的发现相册数据的接口是
https://h5.qzone.qq.com/proxy/domain/photo.qzone.qq.com/fcgi-bin/cgi_list_photo

爬取的时候记得携带自身账号的cookie即刻
编程能力就像任何其他技能一样,也是一个可以通过
刻意练习大大提高的。

经典面试题目清单,算法难度为初级,包括数组和字符串、链表、 树和图、回溯算法、排序和搜索、 动态规划、设计问题、数学、其他九部分内容。这些练习题能够助你温习知识点,进一步沉淀自己的知识。
Given an integer array nums sorted in non-decreasing order, remove the duplicates in-place such that each unique element appears only once. The relative order of the elements should be kept the same.
Since it is impossible to change the length of the array in some languages, you must instead have the result be placed in the first part of the array nums. More formally, if there are k elements after removing the duplicates, then the first k elements of nums should hold the final result. It does not matter what you leave beyond the first k elements.
Return k after placing the final result in the first k slots of nums.
Do not allocate extra space for another array. You must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.Input: nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
Output: 5, nums = [0,1,2,3,4,_,_,_,_,_]
Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums being 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively.
It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
left,right = 0,1
while right <= len(nums) - 1:
if nums[left] == nums[right]:
right += 1
else:
left += 1
nums[left] = nums[right]
return left + 1
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
for i in range(len(nums) - 1, 0, -1):
if nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
del nums[i]
return len(nums)PS:第一种双指针显然是比逆序删除的效率要高的,当然还有正序删除需要处理索引挺麻烦而且效率很低,试了下会超时。
You are given an integer array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
On each day, you may decide to buy and/or sell the stock. You can only hold at most one share of the stock at any time. However, you can buy it then immediately sell it on the same day.
Find and return the maximum profit you can achieve.Input: prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4]
Output: 7
Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 3 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
Then buy on day 4 (price = 3) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-3 = 3.
Total profit is 4 + 3 = 7.class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
mp = 0
for i in range(1, len(prices)):
if prices[i] - prices[i-1] > 0:
mp += prices[i] - prices[i-1]
return mpclass Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
n = len(prices)
if n == 1:
return 0
dp = [[0,0] for _ in range(n)]
dp[0][0] = 0
dp[0][1] = -prices[0]
for i in range(1,n):
dp[i][0] = max(dp[i-1][0], dp[i-1][1]+prices[i])
dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][0]-prices[i])
return max(dp[n-1])PS:这题用贪心要更简单一些,动态规划有点复杂化了把问题,不过可以用来练练
关于DP代码的解释:
定义如下:
dp[i][0]表示第i天手里没有股票的最大利润dp[i][1]表示第i天手里有股票的最大利润我们先想如果当天手里没有股票,只有两种情况,第一种是昨天有的股票今天卖了,这时的利润为dp[i-1][1] + prices[i],第二种是昨天没有股票,今天也没有买股票,这时候的利润为dp[i-1][0],我们需要取最大的情况:
即 dp[i][0]=max(dp[i-1][1] + prices[i], dp[i-1][0])
如果当天手里有股票,也只有两种情况,第一种是昨天的股票在今天没有去卖,利润为dp[i-1][1],另一种情况是今天买了新的股票,利润为dp[i-1][0] - prices[i],我们仍要取最大情况:
即 dp[i][1]=max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][0] - prices[i])
综上所述,我们只需要遍历一遍得到最后一天的手里有股票和没有股票情况下的利润,取最大值即可。
Given an array, rotate the array to the right by k steps, where k is non-negative.Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k = 3
Output: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: [7,1,2,3,4,5,6]
rotate 2 steps to the right: [6,7,1,2,3,4,5]
rotate 3 steps to the right: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]class Solution:
def rotate(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> None:
n = len(nums)
k %= n
nums[:] = nums[n-k:] + nums[0:n-k]class Solution:
def rotate(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> None:
temp = nums[0]
idx = 0
n = len(nums)
vis = [False for _ in range(n)]
cnt = 0
while cnt < n:
idx = (idx + k) % n
if vis[idx]:
idx = (idx + 1) % n
temp = nums[idx]
else:
vis[idx] = True
t = nums[idx]
nums[idx] = temp
temp = t
cnt += 1
PS:第一种方法注意用nums[:]对临时的nums[n-k:] + nums[0:n-k]进行浅拷贝,第二种方法将整个数组看成一个环形,每个元素后移K个位置如图:
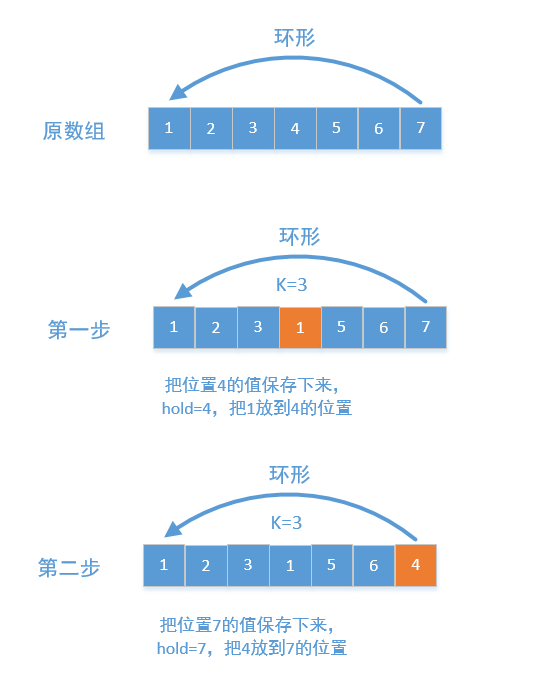
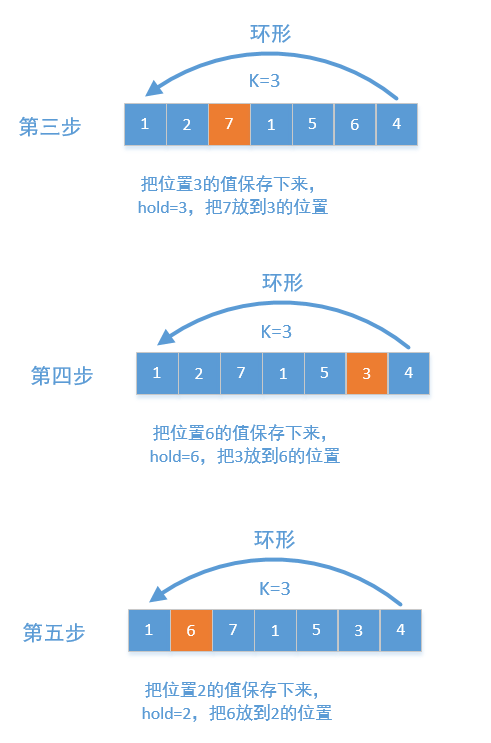
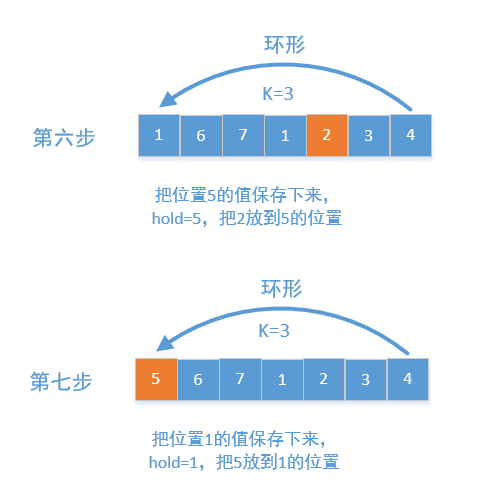
但是这里需要注意如果下一个位置是已经访问过的,会导致无限循环,需要用vis记录当前位置是否已经被访问!
Given an integer array nums, return true if any value appears at least twice in the array, and return false if every element is distinct.Input: nums = [1,2,3,1]
Output: trueclass Solution:
def containsDuplicate(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool:
s = set()
for i in nums:
if i in s:
return True
else:
s.add(i)
return Falseclass Solution:
def containsDuplicate(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool:
nums.sort()
for i in range(1,len(nums)):
if nums[i-1] == nums[i]:
return True
return FalsePS:正常做法应该就是放集合表确定不重复叭,排序效率要低一些,直接暴力的话过不了的。
Given a non-empty array of integers nums, every element appears twice except for one. Find that single one.
You must implement a solution with a linear runtime complexity and use only constant extra space.Input: nums = [4,1,2,1,2]
Output: 4class Solution:
def singleNumber(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
ans = 0
for i in nums:
ans ^= i
return ansPS:位运算应该是最简单的方法了,异或运算我们可以知道:
0 ^ 0 = 0
0 ^ 1 = 1
1 ^ 0 = 1
1 ^ 1 = 0而且异或运算支持交换律,所以出现两次的数字经过连续异或后都最终变成0,0和只出现一次的数字异或的结果就是那个数字本身。
Given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, return an array of their intersection. Each element in the result must appear as many times as it shows in both arrays and you may return the result in any order.Input: nums1 = [4,9,5], nums2 = [9,4,9,8,4]
Output: [4,9]
Explanation: [9,4] is also accepted.class Solution:
def intersect(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]:
m = {}
for i in nums1:
if i in m:
m[i] += 1
else:
m[i] = 1
ans = []
for i in nums2:
if m.get(i) and m.get(i) > 0:
ans.append(i)
m[i] -= 1
return ansclass Solution:
def intersect(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]:
p1, p2 = 0, 0
ans = []
nums1.sort()
nums2.sort()
while p1 < len(nums1) and p2 < len(nums2):
if nums1[p1] == nums2[p2]:
ans.append(nums1[p1])
p1 += 1
p2 += 1
else:
if nums1[p1] > nums2[p2]:
p2 += 1
else:
p1 += 1
return ansPS:两种方法,第一种用哈希表记录元素出现次数应该是最容易想到的方法,第二种先对原数组升序排序,然后用两个指针遍历两个数组,如果指针的两个数组元素相等则加入答案的列表中,如果不同,则让元素值低一些的指针右移即可。
You are given a large integer represented as an integer array digits, where each digits[i] is the ith digit of the integer. The digits are ordered from most significant to least significant in left-to-right order. The large integer does not contain any leading 0's.
Increment the large integer by one and return the resulting array of digits.Input: digits = [9]
Output: [1,0]
Explanation: The array represents the integer 9.
Incrementing by one gives 9 + 1 = 10.
Thus, the result should be [1,0].class Solution:
def plusOne(self, digits: List[int]) -> List[int]:
for i in range(len(digits) - 1, -1, -1):
if digits[i] != 9:
digits[i] += 1
return digits
else:
digits[i] = 0
return [1] + digitsPS:倒着遍历,如果当前数字小于9则对当前元素+1返回即可,如果等于9则置零继续检查更高位,直到遇到小于9的元素,如果遍历完成还未返回,说明这个数组的元素全是9,所以最后需要在数组最前面插入1
Given an integer array nums, move all 0's to the end of it while maintaining the relative order of the non-zero elements.
Note that you must do this in-place without making a copy of the array.Input: nums = [0,1,0,3,12]
Output: [1,3,12,0,0]class Solution:
def moveZeroes(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
for i in range(len(nums) - 1, -1, -1):
if nums[i] == 0:
del nums[i]
nums.append(0)class Solution:
def moveZeroes(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
idx = -1
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] != 0:
idx += 1
nums[idx] = nums[i]
for i in range(idx + 1, len(nums)):
nums[i] = 0PS:逆序删除比较容易处理,但是效率低于第二种方式,第二种方式类似使用指针记录遍历到第几个非0元素了然后直接赋值即可,最后把剩下的部分置零。
Given an array of integers nums and an integer target, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
You can return the answer in any order.Input: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
Output: [0,1]
Explanation: Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1]class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
d = {}
for i in range(len(nums)):
if target - nums[i] in d:
return [d[target-nums[i]],i]
else:
d[nums[i]] = i
return []class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
for i in range(len(nums)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] + nums[j] == target:
return [i, j]
return []PS:有人相爱,有人夜里开车看海,有人 leetcode 第一题都做不出来。
Determine if a 9 x 9 Sudoku board is valid. Only the filled cells need to be validated according to the following rules:
Each row must contain the digits 1-9 without repetition.
Each column must contain the digits 1-9 without repetition.
Each of the nine 3 x 3 sub-boxes of the grid must contain the digits 1-9 without repetition.
Note:
A Sudoku board (partially filled) could be valid but is not necessarily solvable.
Only the filled cells need to be validated according to the mentioned rules.Input: board =
[["5","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."]
,["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."]
,[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."]
,["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"]
,["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"]
,["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"]
,[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."]
,[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"]
,[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]]
Output: trueclass Solution:
def isValidSudoku(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> bool:
row = [[False for _ in range(10)] for _ in range(10)]
col = [[False for _ in range(10)] for _ in range(10)]
grid = [[False for _ in range(10)] for _ in range(10)]
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
if board[i][j] != '.':
if row[i][int(board[i][j])]:
return False
else:
row[i][int(board[i][j])] = True
if col[j][int(board[i][j])]:
return False
else:
col[j][int(board[i][j])] = True
if grid[i // 3 * 3 + j // 3][int(board[i][j])]:
return False
else:
grid[i // 3 * 3 + j // 3][int(board[i][j])] = True
return True
PS:这题暴力的写法可以更优雅一些,不需要这么多的IF,当然这题还有其他方法,想到用位运算做的都是啥天才呀!
You are given an n x n 2D matrix representing an image, rotate the image by 90 degrees (clockwise).
You have to rotate the image in-place, which means you have to modify the input 2D matrix directly. DO NOT allocate another 2D matrix and do the rotation.Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: [[7,4,1],[8,5,2],[9,6,3]]
class Solution:
def rotate(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> None:
for i in range(len(matrix) // 2):
matrix[i], matrix[len(matrix) - 1 - i] = matrix[len(matrix) - 1 - i], matrix[i]
for i in range(len(matrix)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(matrix)):
matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i] = matrix[j][i], matrix[i][j]
PS:观察规律即可,简单的数组操作
Write a function that reverses a string. The input string is given as an array of characters s.
You must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.Input: s = ["h","e","l","l","o"]
Output: ["o","l","l","e","h"]class Solution:
def reverseString(self, s: List[str]) -> None:
h, t = 0, len(s) - 1
while h <= t:
s[h], s[t] = s[t], s[h]
h += 1
t -= 1PS:当然,直接用 reverse 也是可以的💩
Given a signed 32-bit integer x, return x with its digits reversed. If reversing x causes the value to go outside the signed 32-bit integer range [-2^31, 2^31 - 1], then return 0.
Assume the environment does not allow you to store 64-bit integers (signed or unsigned).Input: x = 123
Output: 321class Solution:
def reverse(self, x: int) -> int:
ans = 0
flag = False
if x < 0:
flag = True
x = -x
while x > 0:
ans *= 10
ans += x % 10
x //= 10
return (-ans if flag else ans) if -2**31 <= ans <= 2**31 - 1 else 0class Solution:
def reverse(self, x: int) -> int:
x = str(x)
if x[0] == '-':
x = x[0] + x[-1:-len(x):-1]
else:
x = x[::-1]
x = int(x)
return x if -2**31 <= x <= 2**31 - 1 else 0PS:Python中第二种方法居然比第一种快
Given a string s, find the first non-repeating character in it and return its index. If it does not exist, return -1.Input: s = "loveleetcode"
Output: 2class Solution:
def firstUniqChar(self, s: str) -> int:
m = {}
for i in s:
if i in m:
m[i] += 1
else:
m[i] = 1
for k,v in m.items():
if v == 1:
for i in range(len(s)):
if s[i] == k:
return i
return -1PS:或许用自制的哈希表(两个数组)会更快一些
Given two strings s and t, return true if t is an anagram of s, and false otherwise.
An Anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase, typically using all the original letters exactly once.Input: s = "anagram", t = "nagaram"
Output: trueclass Solution:
def isAnagram(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
if len(s) != len(t):
return False
m = {}
for i in s:
if i in m:
m[i] += 1
else:
m[i] = 1
for i in t:
if m.get(i) and m[i] > 0:
m[i] -= 1
else:
return False
return Trueclass Solution:
def isAnagram(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
a = sorted(list(s))
b = sorted(list(t))
return a == bPS:emm,最好用第一种方法
A phrase is a palindrome if, after converting all uppercase letters into lowercase letters and removing all non-alphanumeric characters, it reads the same forward and backward. Alphanumeric characters include letters and numbers.
Given a string s, return true if it is a palindrome, or false otherwise.Input: s = "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama"
Output: true
Explanation: "amanaplanacanalpanama" is a palindrome.class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, s: str) -> bool:
s = [_ for _ in s if _.isalpha() or _.isdigit()]
left, right = 0, len(s) - 1
while left <= right:
if s[left].lower() != s[right].lower():
return False
left += 1
right -= 1
return TruePS:注意题目中的 “removing all non-alphanumeric characters” 先去除所有的非字母数组后验证回文,类似反转字符串的双指针操作。
Implement the myAtoi(string s) function, which converts a string to a 32-bit signed integer (similar to C/C++'s atoi function).
The algorithm for myAtoi(string s) is as follows:
Read in and ignore any leading whitespace.
Check if the next character (if not already at the end of the string) is '-' or '+'. Read this character in if it is either. This determines if the final result is negative or positive respectively. Assume the result is positive if neither is present.
Read in next the characters until the next non-digit character or the end of the input is reached. The rest of the string is ignored.
Convert these digits into an integer (i.e. "123" -> 123, "0032" -> 32). If no digits were read, then the integer is 0. Change the sign as necessary (from step 2).
If the integer is out of the 32-bit signed integer range [-2^31, 2^31 - 1], then clamp the integer so that it remains in the range. Specifically, integers less than -2^31 should be clamped to -2^31, and integers greater than 2^31 - 1 should be clamped to 2^31 - 1.
Return the integer as the final result.
Note:
Only the space character ' ' is considered a whitespace character.
Do not ignore any characters other than the leading whitespace or the rest of the string after the digits.Input: s = " -42"
Output: -42
Explanation:
Step 1: " -42" (leading whitespace is read and ignored)
^
Step 2: " -42" ('-' is read, so the result should be negative)
^
Step 3: " -42" ("42" is read in)
^
The parsed integer is -42.
Since -42 is in the range [-231, 231 - 1], the final result is -42.class Solution:
def myAtoi(self, s: str) -> int:
idx = 0
for i in s:
if i != ' ':
break
idx += 1
if idx == len(s):
return 0
sign = 1
if s[idx] == '-' or s[idx] == '+':
if s[idx] == '-':
sign = -1
idx += 1
ans = 0
for i in range(idx, len(s)):
if not s[i].isdigit():
break
else:
temp = ans
ans *= 10
# if ans // 10 != temp:
# return 2 ** 31 - 1 if sign else -2 ** 31
# 如果你用的语言int为32位,需要在这里提前判断越界,py就无所谓了
ans += int(s[i])
return ans * sign if -2 ** 31 <= ans * sign <= 2 ** 31 - 1 else (2 ** 31 - 1 if sign == 1 else -2 ** 31)PS:按照题目要求慢慢判断就行了,注意越界要提前判断,py的话可以在最后判断。
Implement strStr().
Given two strings needle and haystack, return the index of the first occurrence of needle in haystack, or -1 if needle is not part of haystack.
Clarification:
What should we return when needle is an empty string? This is a great question to ask during an interview.
For the purpose of this problem, we will return 0 when needle is an empty string. This is consistent to C's strstr() and Java's indexOf().Input: haystack = "hello", needle = "ll"
Output: 2class Solution:
def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
h = 0
n = 0
while h < len(haystack):
if haystack[h] == needle[n]:
h += 1
n += 1
if n == len(needle):
return h - len(needle)
else:
h -= n
h += 1
n = 0
return -1
今天是八月二十六日,距离开学还有一天的时间,这个假期算是过的比较充实的了吧,呜呜又是学车又是做项目,一直到八月十几号才彻底放假,不过到这时候,也快开学啦。
『MingJiaAPI』
一个简单运维管理系统
这个项目其实在上个学期一开学就开始了,整个项目就是一个公司的运维管理系统,负责对公司的产品进行售后服务,维修之类的,包括对设备的管理,维修订单的分析记录,还有工程师的绩效考核等功能。本来是上个学期我和一个学长负责的,后来干了一个来月,甲方的母公司想和原有的系统结合做成大数据人工智能的大平台,想用JAVA开发,然后就暂时搁置了,因为俩学生干不了。
后来快放假的时候,老师联系我们,甲方母公司弄了一圈不打算干预了,然后按照原定计划继续开发就行了。然后我又拉了个同学来做小程序端的开发,因为我实在是懒得写前端~
假期一放假就开始了这个项目的开发,顺便做了一个重大的决定,推翻之前的后端架构,全部重写了,呜呜现在回想起来,幸亏一放假就重构了项目,要是按照之前的架构写下去估计后面得写崩溃。一开始我们是用的Flask做Api,数据库模型用的我之前自己封装的烂轮子,emm其实还行,就是效率确实不怎么高。架构做的也很随便,主要是代码写的太乱了,一开始没有做好风格规范,我用小驼峰,他用大驼峰,我用小写下划线,他用大写下划线,后面写的一堆东西都看不懂了,数据库的字段命名也是有大写有小写有下划线有驼峰的,所以在这次假期开工的时候,直接删库重做了!
之前的小程序界面貌似也发过日记,在这里呢:微信小程序,那时候刚开始学小程序,做的真的挺丑的!
放假之后,我决定换新的架构,这次用的FastApi做后端,数据库模型直接用Tortoise-orm,俩异步框架的效率果然还是很快的,我和学长大概用了两三天时间把小程序端的所有功能的API做完了,结果发现最难的不是开发,而是对接口,新来的前端同学一开始不熟悉这个项目,看不懂我们的接口,所以我们用了一个多星期的时间和前端对接,前端通过腾讯会议共享屏幕,我们直接口述接口和所有参数的意义,当然后面也做了相应的文档,对接过程中还是发现了不少BUG,一遍改一遍对,终于在一周后对接完成了。不过这只是成功了一小部分。



因为这个项目小程序只是其中一部分,还需要一个后台管理系统,之前其实也没做过后台管理系统,毕竟之前开发的小玩意都是自己做着玩的,没完整的开发过一次后台系统(主要是懒得做) 这里一开始想的是让前端同学用Vue做界面,然后我和那个学长继续开发Api,后来我俩商量一番,干脆直接搞全栈算了,让前端继续完善小程序的使用体验,所以最后,我俩直接在FastApi的基础上,用Jinja2做,加上adminlte框架,做了大概一两周也把后台完整的开发出来啦
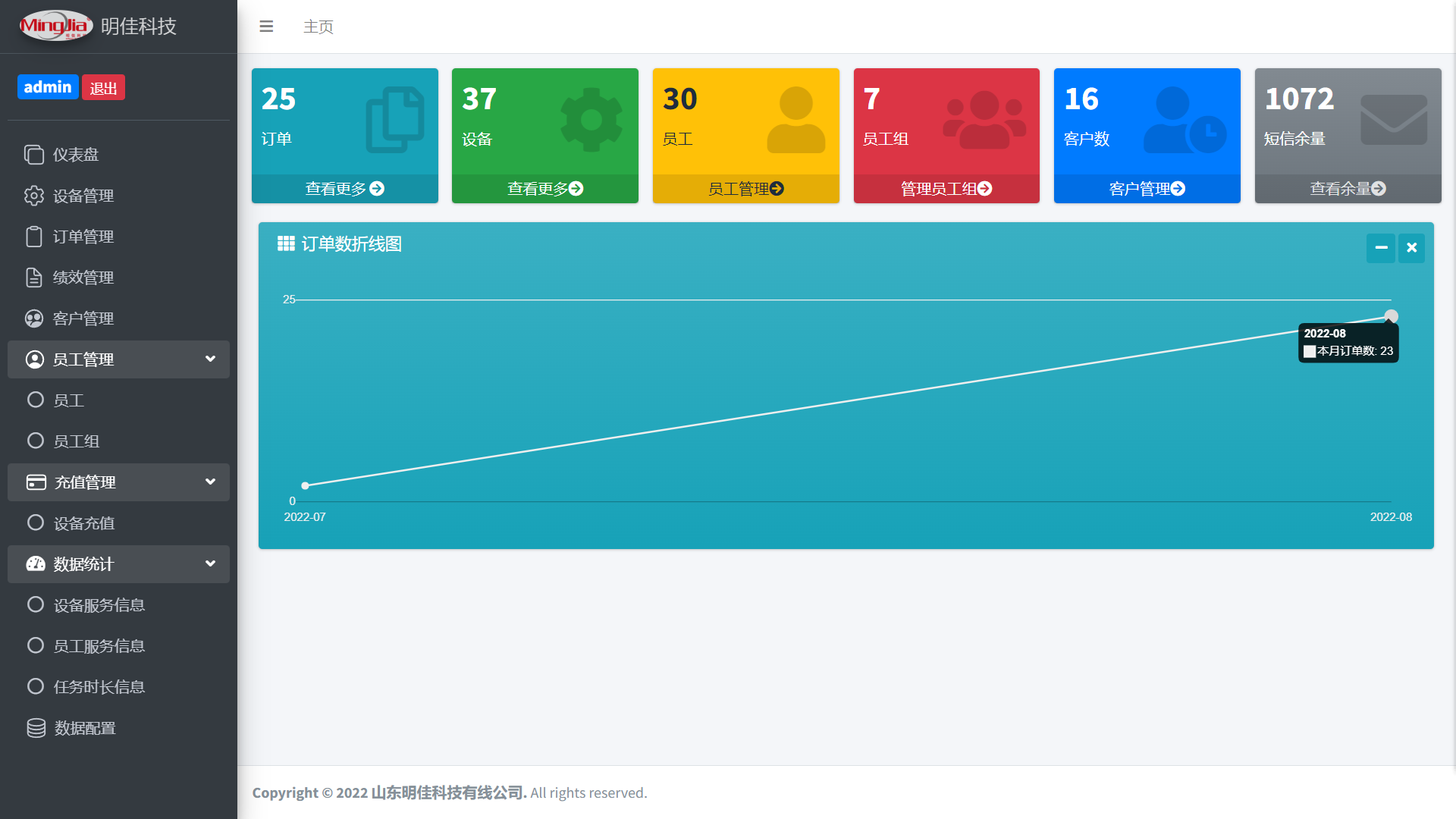

做后台的时候印象最深的就是sql了,上学期刚学了数据库原理,这算是复习了嘛,因为python的Tortoise数据库模型框架的功能不够强大(其实已经很强了),但是还是需要一些额外的功能,只能通过手动sql来实现啦。
在这个项目过程中还遇到了一些问题,也不是大问题一会就解决了,一开始甲方想要维修订单的通知,微信小程序通知加短信通知,但是看了下小程序的相关条例,微信通知权限一次授权只能通知一次,长期的通知不太好申请到权限,最后商量只做了短信的通知,用的腾讯云的短信服务,他们的SDK还挺齐全的。最后我想说,adminlte框架确实太舒服了,如果是全栈开发后台的话,首选它就完事了!
『科目三』
🏊👏🍺⭐
暑假终于考完了科目三,还是很顺利的!从7月20号开始练车,练到了7月21号就约了29号的考试,然后就在家玩了,等到考试前一天去考场熟悉考场,每条路线模拟了一次,考试一把满分过啦,呜呜,我好聪明。

『刘兰婷』
你是落在我世界里的一束光
我们很多次说过想想咱俩会在一起真的挺离谱了,毕业两年后没怎么联系,突然在上个学期的末尾在一起啦!
上个学期你放假的时候,我们像是网恋奔现一样,两年没见,你还是没有太大的变化嘛,除了变漂亮的一些!

见面之后好像越来越喜欢你了,假期里每天都会打电话,会在电话里陪你睡觉,你还说之前不理解为啥情侣还要打着电话睡觉,现在打变成电话睡觉真香了,还天天不让我睡觉!嘿嘿不过也挺好的~我也喜欢和你晚上闭着眼睛聊天.
第一次见面之后我就准备考试周啦,到咱下次见面得有半个月了,呜呜不过因为准备考试没有因为见不到你太难受。7月10号,终于放假回家啦,我们见了一面,不过有些匆忙,吃了个饭就回家啦。
刚放假的那段时间,没有和你见面的每一天都很漫长,而见到你的每一天过的都很快,呜呜,你说自从见面之后就越来越喜欢我了,我也是!有时候就会特别特别想你,就想立刻马上就去见到你,还好咱俩假期能见面,开学也能见面,虽然异地,但是异地的也不远嘛。
七月十五日
水边咖啡,金海歌,新华书店···



七月十九日
电影院,人生大事,红石湖公园···



七月二十四日
投影房,以年为单位的恋爱···
呜呜,这一天忘记拍照啦
八月二日
白裙子,麻辣香锅,瑞幸咖啡,图书馆···




八月六日
在七夕节和你的生日之间,火锅,蛋糕,银手镯,电影,情侣衫,单肩包




这是你的农历生日,可惜我不能陪你过你的阳历生日啦,二十七号的我就已经在学校啦,呜呜,我很喜欢你送我的七夕礼物,刚打开的时候超级感动,看到准备的盒子,还有里面的东西还有你写的字,好好看!还很贴心的说明礼物的作用,呜呜好聪明。
八月十一日
烤肉,秋天的第一杯奶茶···



这次见面之后,我们的下一次见面居然隔了半个月,呜呜,你要开始学车啦
八月二十四日
苍源河公园,拌饭···


这也看来,我们这个假期还是见了挺多次的,开学之后可能就要一个月见一两三次了,😭有时候见不到真的会特别想你的,和你在一起有一种很舒服的感觉,我们之间好像什么都能聊,互相理解对方的心思,啊啊啊就是一种很和谐的感觉,因为咱来的观念比较一致叭,呜呜真好能遇见你并且和你在一起!
『杂』
一些其他的事情
这是正在开发的情侣空间(恋爱圈),界面有点像(抄袭)微信的朋友圈

假期里还和高中朋友,初中朋友聚了聚,唱歌,吃饭,回母校参观

